Understanding how to connect batteries in series and parallel is essential for optimizing power systems. Whether you're working on a DIY solar project or trying to enhance your device's performance, knowing the difference can help you achieve your desired power output effectively.
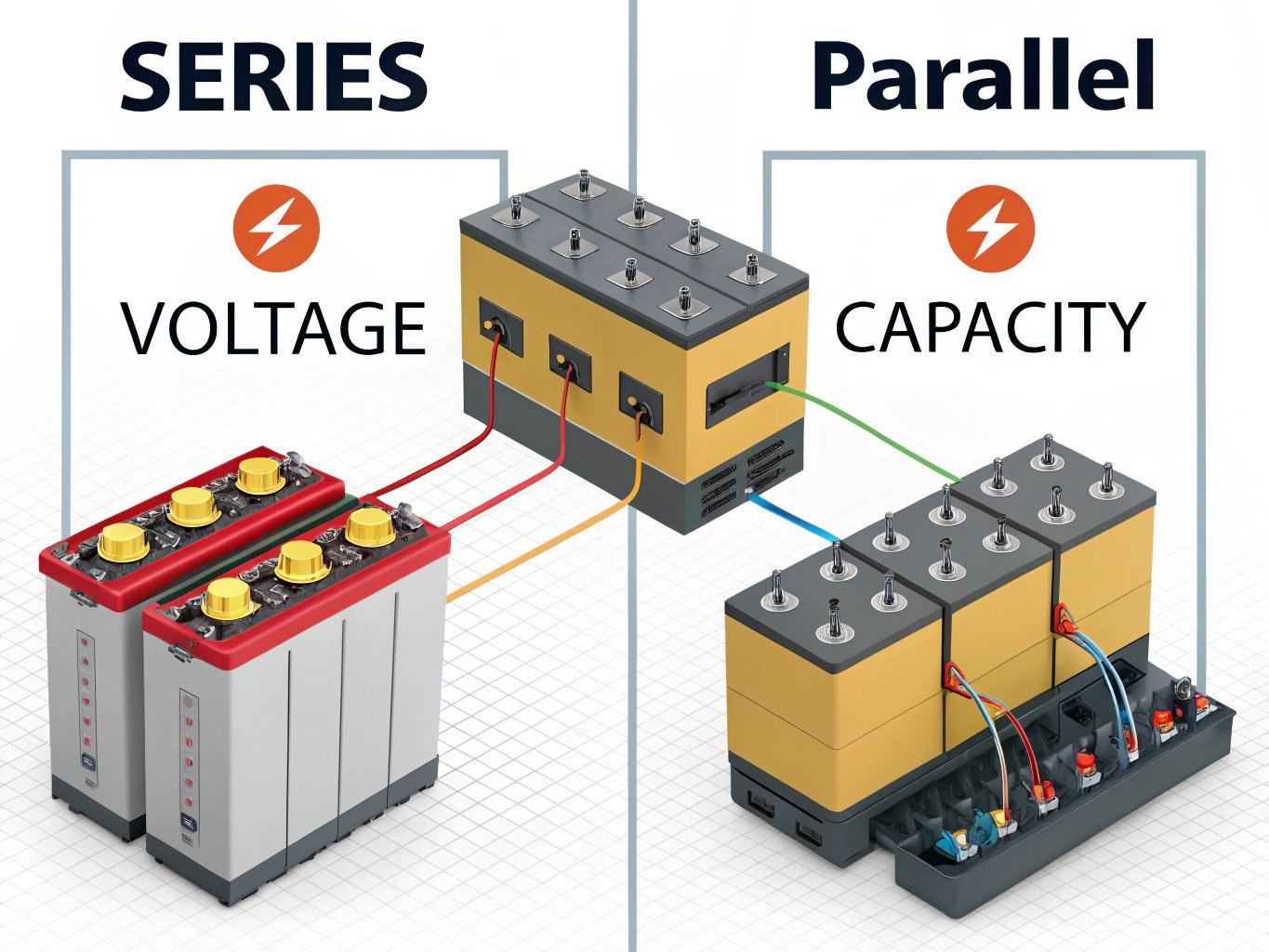
Connecting batteries in series increases the total voltage while maintaining the same capacity (Ah), making it ideal for applications requiring higher voltage levels. Conversely, connecting batteries in parallel maintains the same voltage but increases the overall capacity, allowing for longer operation times. Understanding these configurations is essential for designing efficient power systems in applications ranging from portable electronics to renewable energy storage and electric vehicles. Proper balancing and management of battery connections ensure safety, longevity, and optimal performance.
When building or upgrading power systems, choosing the right battery configuration is critical to meet specific energy demands. Batteries are often connected in series or parallel to adjust the overall voltage or capacity. But what’s the difference? Let's dive deeper into how each connection works and how you can apply them effectively to your projects.
✔
When batteries are connected in series, their voltages add up while the total capacity (amp-hours) remains the same, making them useful for high-voltage applications.
✖
Batteries connected in parallel do not increase voltage; instead, they increase total capacity (amp-hours), extending battery life but maintaining the same voltage level.
Understanding Battery Connections
To start, it's important to understand the basic concept of how batteries work. A battery stores electrical energy in the form of chemical energy, and when connected to a circuit, this energy is released as electrical power. The configuration in which you connect multiple batteries—whether in series, parallel, or both—determines the total voltage and capacity of the system.
- Series Connection: The positive terminal of one battery is connected to the negative terminal of another. This increases the total voltage of the battery array.
- Parallel Connection: The positive terminals are connected together, and the negative terminals are also connected. This maintains the voltage of one battery but increases the total capacity (amp-hours).
Understanding these connections allows you to design the power system that best fits your needs.
How to Connect Batteries in Series
When you connect batteries in series, you increase the total voltage of the battery array. However, the capacity remains the same as that of a single battery. This is ideal when you need more voltage but don’t necessarily require more capacity.
Steps to Connect Batteries in Series:
- Identify Battery Terminals: Each battery has a positive (+) and negative (-) terminal.
- Connect Positive to Negative: Connect the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of the next battery. Continue this pattern for as many batteries as needed.
- Final Connections: The remaining positive and negative terminals will give you the total voltage of the connected batteries.
- Check the Voltage: The total voltage is the sum of all individual voltages (e.g., if each battery is 1.5V and you connect 4 in series, the total voltage will be 6V).
Example:
If you connect four 1.5V batteries in series, the total voltage will be 6V (1.5V + 1.5V + 1.5V + 1.5V), but the total capacity will be the same as one battery's capacity.
How to Connect Batteries in Parallel
Parallel connections are used when you want to increase the battery capacity (amp-hours) without changing the voltage. This is ideal for systems that need long-lasting power, such as in solar power systems or large battery storage.
Steps to Connect Batteries in Parallel:
- Identify Battery Terminals: Again, locate the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals.
- Connect Positive to Positive: Connect all the positive terminals of the batteries together.
- Connect Negative to Negative: Similarly, connect all the negative terminals of the batteries together.
-
Final Connections: The voltage remains the same as a single battery, but the capacity will be the sum of all the batteries' capacities.
Example:
If you connect four 1.5V batteries in parallel, the total voltage will remain 1.5V, but the capacity will be four times the individual battery capacity.
When to Use Series or Parallel Connections
Choosing whether to connect your batteries in series or parallel depends on your energy needs.
- Series Connection:
- Increases voltage.
- Ideal for high-voltage applications such as electric vehicles or high-power devices.
- Parallel Connection:
- Increases capacity (amp-hours).
- Used in solar power systems and energy storage applications.
In some cases, you may need to use a combination of both series and parallel to get the right voltage and capacity for a larger system.
Safety Tips for Connecting Batteries
When connecting multiple batteries, safety is crucial to avoid damage or potential hazards like short circuits or fires.
- Ensure Proper Battery Ratings: Only connect batteries with the same voltage and capacity ratings.
- Use the Correct Wiring: Always use wires rated for the appropriate current and voltage.
- Avoid Short Circuits: Double-check your connections to prevent accidental shorts.
- Use Fuses or Circuit Breakers: Always install fuses or circuit breakers to protect the battery pack from overloads.
Benefits of Using Series and Parallel Connections
Both series and parallel connections have their unique benefits, depending on the system requirements:
Series Connection Benefits:
✔ Increases voltage
✔ Ideal for high-voltage applications
✔ Used in devices like flashlights, electric vehicles, and power tools
Parallel Connection Benefits:
✔ Increases capacity
✔ Extends battery life for prolonged use
✔ Ideal for solar storage systems and off-grid power solutions
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When connecting batteries, there are some common mistakes that can lead to inefficiencies or damage:
- Mixing Different Battery Types: Always use identical batteries in terms of brand, type, and charge level.
- Incorrect Wiring: Ensure the batteries are connected correctly to avoid damaging the batteries or the device they power.
- Overloading the System: Always check that the total voltage and current are within the safe limits of the system you are powering.
Conclusion
Connecting batteries in series and parallel is a crucial aspect of building a reliable power system. By understanding the differences between these two configurations, you can optimize the performance of your power systems.
- Series connections increase voltage, which is ideal for high-power applications.
- Parallel connections increase capacity, allowing for longer-lasting power storage.
Whether you're working on a solar energy project or enhancing the battery capacity of an electronic device, the right battery connection can make all the difference. Always prioritize safety and ensure your battery system meets the required specifications for your application.




